Instance Type Management
Instance type management provides the capabilities of managing a cluster of the computation resources by instances management such as create, delete, edit instances and of permission-control which allows only specified-groups to use the instances.
Creating New Instance Types

Click Add to add an Instance Type, which will pop up the editing screen of Instance Types.

You need to fill in the fields of Basic Info in the above picture:
NameOnly lowercase letters, numbers, hyphen-and a dot.can be filled in.Display nameThe display name of this Instance Type, and will be seen by users.DescriptionThe description of this Instance Type, and will be seen by users.CPU Limitdefine how many CPU are allowed to use by this Instance Type. The value is also applied to CPU Request whenCPU Requestis disabled.Memory Limitdefine how many memory are allowed to use by this Instance Type. The value also applied to Memory Request whenMemory Requestis disabled.GPU Limitdefine how many GPU can be used by this Instance Type. GPU can only be integer.GPU Resource Namedefine which type of GPU is going to be used, you can specifyamd.com/gpuornvidia.com/gpu. TheGPU Limitmust be larger than 1 to enable this field.

Overcommitting (advanced feature)
CPU Requestdefine how many CPU are requested to use by this Instance Type initially. Once it is enabled, instances are guaranteed to get the amount of CPU they request. IfCPU Request<CPU Limit, the system will try to overcommit CPU resources within the limit if more resources are available.Memory Requestdefine how many Memory are requested to use by this Instance Type initially. Once it is enabled, instances are guaranteed to get the amount of Memory they request. IfMemory Request<Memory Limit, the system will try to overcommit Memory resources within the limit if more resources are available.
For details, please see Quality of Service for Pods and Resource QoS.
GlobalIf it is turned on, this Instance Type can be chosen by everyone. You can grant permission to specific groups in theEdit Groups.
Finally, click Confirm to complete the addition.
Toleration
When a node has a taint for certain reasons, an instance won't be scheduled to run on that node until an instance has a specific toleration to tolerate specified taint. Here we will show you how to add a toleration only.
For more detail and usage of kubectl taint, please refer to Taints and Tolerations concept.
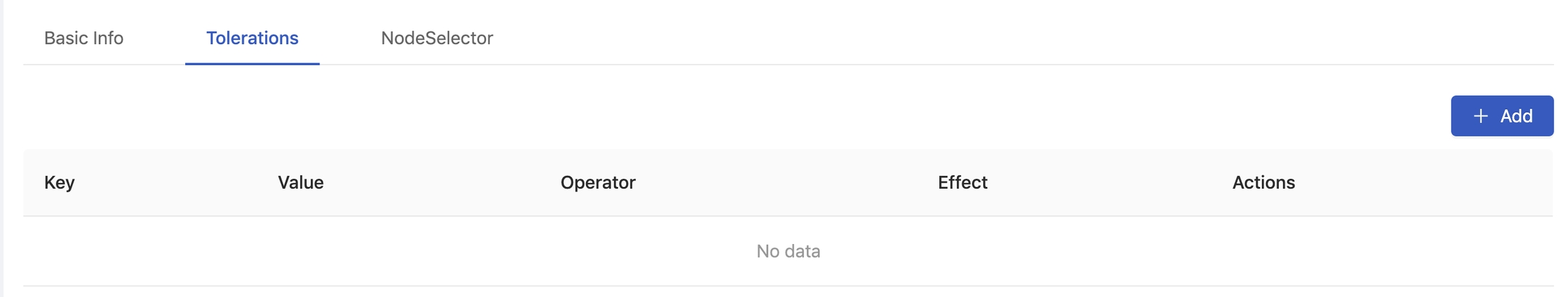
In Toleration tab, you can add a Toleration by clicking on Add button.
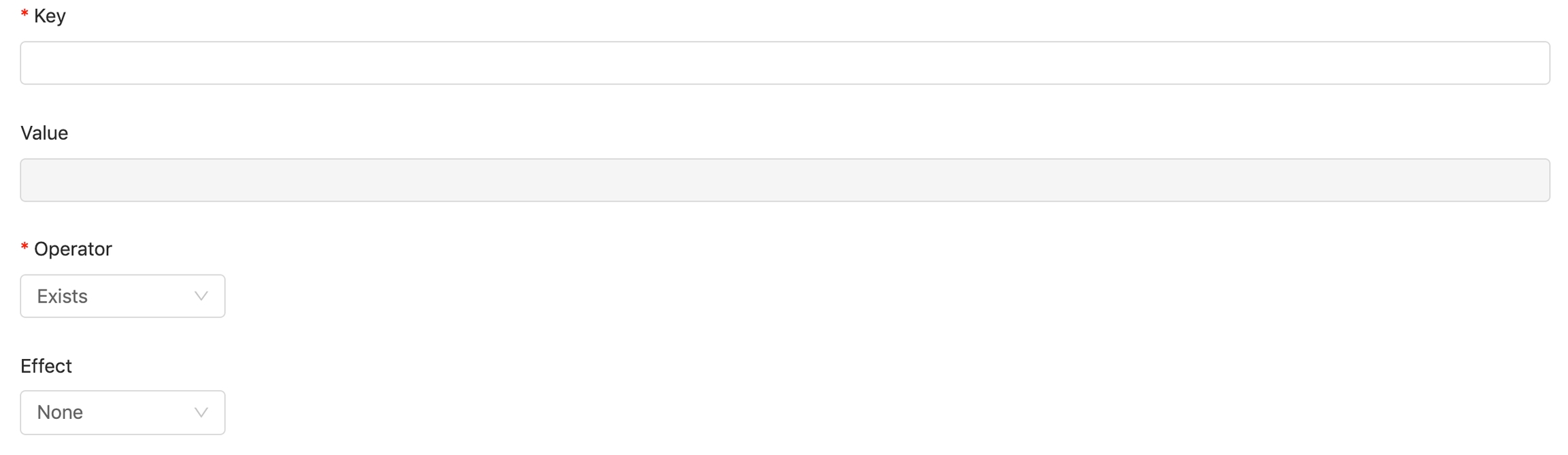
Filling in the fields in popup to create a toleration.
KeyThe key of taint which you want to tolerate.ValueThe value of taint is required ifEqualfromOperatoris selected.Operator (Mandatary)SelectEqual,Exists.EffectSelectNone,NoSchedule,PreferNoSchedule,NoExecute
Regarding options of Operator and Effect, please refer to Taints and Tolerations.
Click OK to add a toleration.
Finally, click Confirm to complete the addition.
For a use case of toleration, please see Toleration Use Case.
Node Selector
You can constrain an instance to only be able to run on specific nodes which have specific labels. A label is a map of key-value pair. Here we will show you how to add a nodeSelector only.
For more detail, please refer to Assigning Pods to Nodes for usage kubectl label.
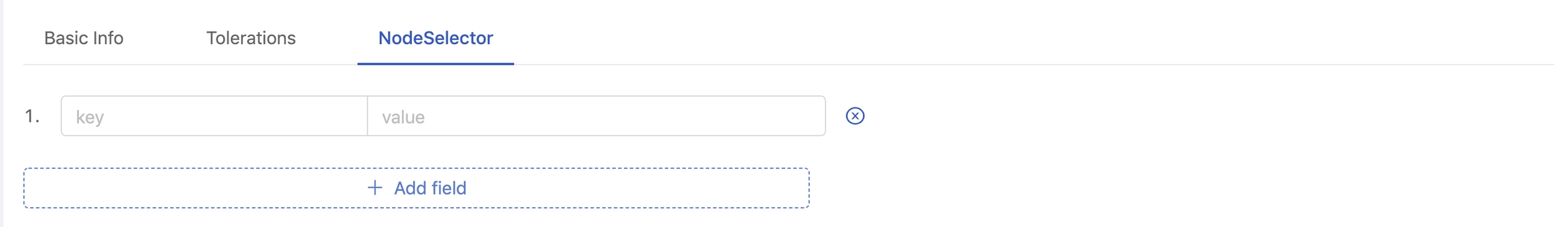
In Node Selector tab, you can add a NodeSelector by clicking on + Add field button.
Filling in key/value with key-value of a label you want to specify.
Click Confirm to complete the addition.
For a use case, please see Node Selector Use Case.
Edit Groups

If Global is disabled, please click Edit Groups under the edit Instance Type screen to select the groups that have permission to use the Instance Type.
Last updated