Job Submission
Allow users to submit machine learning training jobs to the cluster
Features
Job Queue: Job is processed by the order of a queue. And one group has one queue.
Image and InstanceType: Just like jupyter notebook, a user can select the preset images and instance types according to the currently selected group
Shared Volume: The job's running pod would mount the shared volume according to the selected group.
Cancellation: Allow to cancel a pending or running pod
POD Time-To-Live: Allow to clean up the pod after a job is finished for a period of time.
Memory Setting
Job submission controller uses 512Mb memory at most by default. Under this setting, it can record around 50 thousand job history. Please delete some old phjob records if you found phjob records are near 50 thousand. Otherwise, it will run out of memory and cannot work appropriately.
If you want to record more job history, please increase/add the memory setting in helm_override/primehub.yaml, for example:
controller:
resources:
limits:
memory: 5GiDesign
Custom Resource
A custom resource PhJob is defined for PrimeHub-defined job. The job is very similar to the kubernetes native job, the controller would spawn a pod for the job's spec. The difference is that the spec contains the PrimeHub-specific concept, like group, image, instance type.
Here is an example of PhJob.
apiVersion: primehub.io/v1alpha1
kind: PhJob
metadata:
name: job-qm42d
namespace: hub
spec:
command: |
echo "start"
displayName: Test Job
userId: 619156fe-43c6-44f3-b20e-2d5f96e4df96
userName: jackpan
groupId: d8257cb0-3c89-4243-98c2-cdc737ec61d3
groupName: test-job-submission
image: base-notebook
instanceType: cpu-tiny
status:
phase: pendingState Diagram
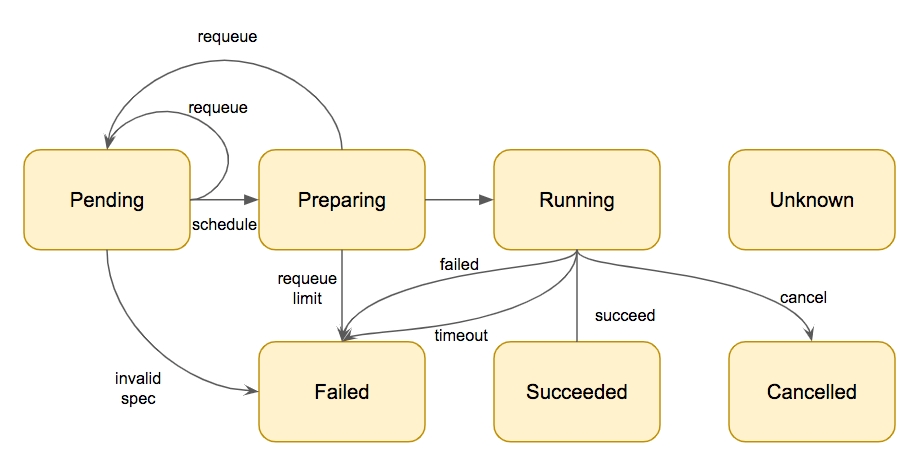
There are 6 states for the PhJob
Pending: Job is pending in the queue
Preparing: The job is dequeue and ready to be processed. The underlying pod is created and waiting for scheduled and initiated.
Running: Pod is running
Failed: Pod is failed.
Succeeded: Pod is terminated successfully.
Cancelled: The job is Canceled
Scheduler
Unlike kubernetes' job, PhJob is scheduled by the controller rather than the scheduler. And only when the resource is ready is the pod created. Here is the basic principle for scheduling
Group is a logical queue. Jobs in the same group is scheduled in the FIFO (first in first out) manner
Resource constraint: Job is scheduled only when it doesn't hit the group quota and user quota. And if a job has no enough resources in user quota, it will not block other jobs belong to other users.
Resource Pool: Both the jupyter server and job share the same resource pool.
Pod creation: pod is created as the job is scheduled.
State change: once a job is scheduled, the state is changed from
pendingtopreparing
Here are some examples of the scheduling behavior.
Example 1
There are three jobs submitted to the same group phusers. Assume that the group setting is
User quota: 4 gpu
Group quota: 4 gpu
And the job specs are
A
2
bob
B
4
pan
C
2
lin
Results
A
2
bob
Preparing
B
4
pan
Pending
C
2
lin
Pending
Job B is blocked because of no enough GPU. Job C is blocked by job B because the job is scheduled by FIFO.
Example 2
The same as example 1, there are three jobs submitted to the same group phusers. And the group setting is also
User quota: 4 gpu
Group quota: 4 gpu
The job specs are
A
2
bob
B
4
bob
C
2
lin
The only difference is the job B is also submitted by bob. The result is
A
2
bob
Preparing
B
4
bob
Pending
C
2
lin
Preparing
Job B is blocked because of no enough GPU. Job C is scheduled because job B is blocked by user quota rather than group quota. If the user quota is not enough, the job is not eligible to block other jobs belong to other users.
Requeue
After a job is scheduled, the underlying pod is created. However, according to the pod lifecycle design, a pod does not run immediately until the job is assigned to a node and the containers are initiated. If a pod cannot reach to running state for a given time (default 3 minutes), the job is pushed back from preparing state to pending state and wait for next scheduling.
Running Pod
Here describe what the underlying pod would look like. The pod is generated according to the selected group, image, and instance type. It determines what image to use, how many resources to request, and how many volumes should be mounted.
Folder Structure
The primary volumes and locations are
Working Directory
/home/jovyan
Is mounted as emptyDir
Volumes
/datasets/<volume-name>
symlink to /home/jovyan/datasets
Group Volume
/project/<project-name>
symlink to /home/jovyan
User Volume
N/A
├── datasets
│ ├── ds1
│ ├── ds2
│ └── ds3
├── project
│ ├── group1
│ ├── group2
│ └── group3
└── home
└── jovyan
├── datasets -> /datasets
│ ├── ds1
│ ├── ds2
│ └── ds3
├── group1 -> /project/group1
├── group2 -> /project/group2
└── group3 -> /project/group3The working directory is mounted as an emptyDir so that users can put temporary data under the folder.
Compare to Jupyter Pod
user volume
Yes
No
group Volume
Yes
Yes
pv data volume
Yes
Yes
pv data volume (hostpath)
Yes
Yes
env data volume
Yes
Yes
git data volume
Yes
Yes
working directory
/home/jovyan (user volume)
/home/jovyan (emptyDir)
start-notebook script
Yes
No
Log
The job log is not stored externally. Instead, the log is retrieved by the underlying pod. So to retrieve the log, just
kubectl -n hub log job-20200101-12345Environment Variables
There are these environment variables defined in the running jobs.
PRIMEHUB_USER
The user to submit the job
PRIMEHUB_GROUP
The launch group of the job
Timeout
To prevent the job from running a too long time, there is a default timeout 1 day. The timeout can be configured by
Overwrite
PhJobspec.spec.activeDeadlineSecondsOverwrite the helm value
jobSubmission.defaultActiveDeadlineSeconds
Cancellation
A job can be canceled in the non-final state. To cancel a job, just set the PhJob .spec.cancel to true. If a job is canceled, the underlying pod is deleted.
Pod TTL After Finished
A pod is a heavy resource for these two reasons
Log
Overlay storage
Even though the container is terminated, these two resources are not released until the pod is deleted.
To make the operator easier to reclaim the resources, we can configure the TTL of Pods. The default value is 7 days. This can also be configured by
Overwrite PhJobs spec
.spec.ttlSecondsAfterFinishedOverwrite the helm value
jobSubmission.defaultTTLSecondsAfterFinished
Administrator
Working Directory Size
The working directory is mounted to a emptyDir volume. By default, the capacity is 5Gb. The default value can be changed by the helm value.jobSubmission.workingDirSize
Default Pod Scheduling
It is desired to limit the job only run on a specific node. We can configure the default nodeSelector, affinity, tolerations for created pod.
Performance Issues
It is a known issue that there might be some performance issues when phjob has more than 10 thousand records. For example, the job submission page or jupyter spawner page takes a longer time to respond. If you notice this situation, please try to delete old phjob records and see if it alleviates the situation.
FAQ
Q: Can one group run more than one jobs at the same time?
Yes. If the job have not reached the user quota and group quota
Q: Why jobs are not run in the right order?
The lifecycle of a job is from pending, to preparing, then running. We only guarantee that jobs enter the preparing state in the order of the job creation time. After a job is preparing, we cannot guarantee that the job goes to the running state in the same order. For example, one job takes a longer time to pull an image than another one does.
Q: Why are all my jobs stuck in the preparing state?
This is because the pod cannot be initiated for some reason. Please ask the operator to see what happens to the underlying pod. One common reason is the cluster has no enough resources for this pod.
Q: Does a job enter preparing state only when the cluster has enough resources?
No. The only criteria if a job enters the preparing state are if there are enough user and group quota. That is, it is still possible that the pod cannot be scheduled because no node can fit the submitted job.
The administrator should plan the instance type, user quota, group quota carefully to prevent resource over-commit happens.
Q: Can I kill a job?
Yes. But currently, we only allow users to delete a job from kubectl. The command is
kubectl -n hub delete phjob <job name>As the phjob is deleted, the underlying pod is deleted as well.
Q: Why can't I see the log?
From the UI, the log is retrieved in the same way of kubectl -n hub logs <podname>. So if you cannot see the log, the reason could be
The underlying pod is not created or deleted
The log of the pod is deleted, truncated, or rotated for docker daemon.
If a job is canceled or timeout, the log cannot be retrieved because the underlying pod is deleted. This is the current limitation and we hope we can preserve the log in the future.
Q: What happens if my job runs on a lost node?
If a pod is running on a lost node (which shows NotReady status on the kubectl get nodes), the pod status will change to Unknown status in 5 minutes. At this moment, the job is still in the Running state. However, the job detail pages may show the following message and the log cannot show correctly.
Status: Running
Message: Node <node-name> which was running pod <job-id> is unresponsiveIt should be noted that the resources for this job are not released.
What we can do is
Just cancel the job, then the job resources will be released. And re-run the job if necessary.
Ask operators to recover the lost node. Once the node is recovered, the pod can still run.