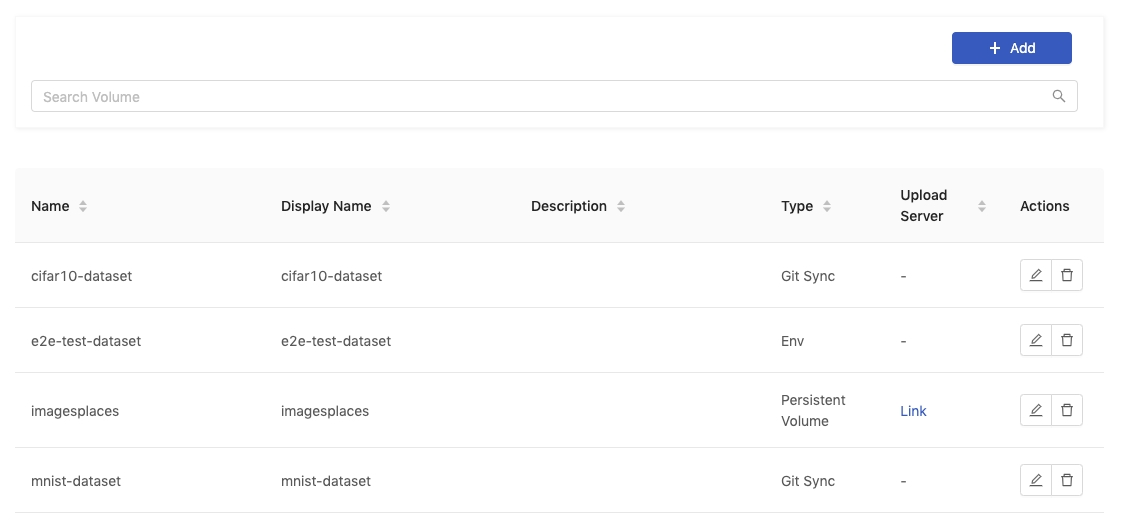
Volume Management
Volume management provides the capabilities of managing volume resources such as create, delete, edit volumes and of permission-control so that volumes can be accessed only by specific groups accordingly.
Creating New Volume
Click Add to add a Volume and it will pop up the edit screen of Volumes.
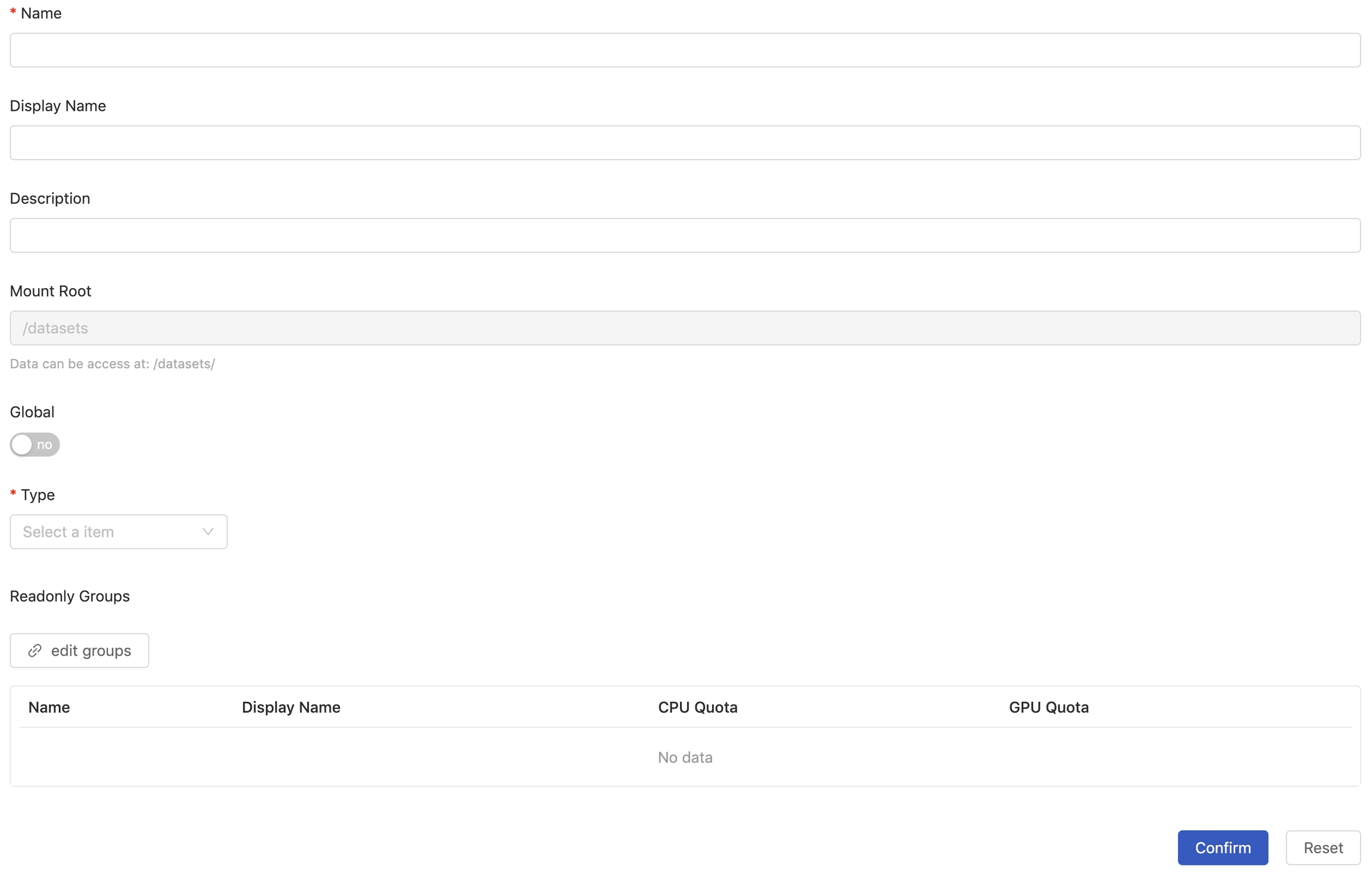
You need to fill in these fields:
Name(required): Only lowercase letters, numbers, hyphen-and a dot.can be filled in.Display nameDescriptionMount RootThis field is not editable. It displays the path to volumes.GlobalIf enabled, everyone can read this volume; furthermore, we can setWritablegroups. If disabled, linking groups withReadOnlyorWritablepermission byedit groupsis required.TypeVolume type.Edit GroupsSet accessible groups, whenGlobalis disabled.
There are several type:
Persistent Volume
Provisioning:Auto,Manual.
Auto
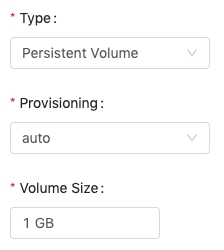
Specifying the volume size, once it is confirmed, there is a fixed-size volume created and the volume size is not changeable by editing the volume.
Manual
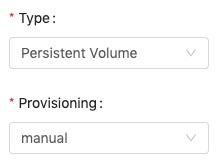
Setting provisioning Manual allows administrators configure the persistent volume manually with an existing storage. Generally, it is used for storages types which are not listed in PrimeHub Volume. Please refer to the Kubernetes official documentation for the configuration.
The only rule you need to follow is that the PersistentVolumeClaim name must be volume-{"Name" field set via UI}.
Click Confirm to complete the addition.
NFS
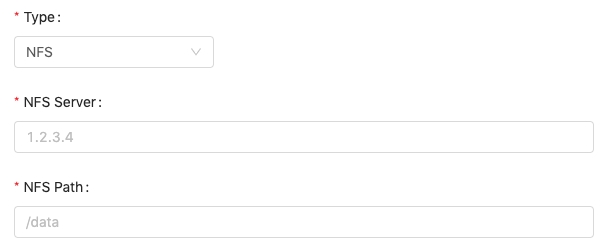
An nfs volume allows an existing NFS(Network File System) share to be mounted into the pod. The data of an nfs volume is preserved even if the volume is unmounted. NFS can be mounted by multiple groups simultaneously.
NFS settings remain editable after the creation.
NFS ServerFill in the URL of the server.NFS PathFill in the path to the share.
Host Path

In PrimeHub, a hostPath volume mounts a directory from the hosting node's filesystem into the pod.
The hostpath/to/directory must exist on nodes and corresponding permissions must be granted, otherwise unexpected behaviors which are varied with circumstances occur. Please see trouble-shooting.
HostPathFill in the path to a directory. The setting remains editable after the creation.
Git Sync
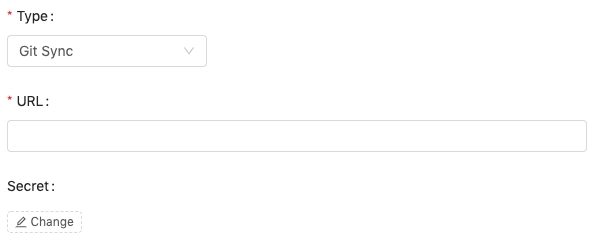
Fill the URL of git repo (can be https or git). You can use #branch to specify the branch or tag name.
Click Change to select a secret from the list if a credential is required.

Env
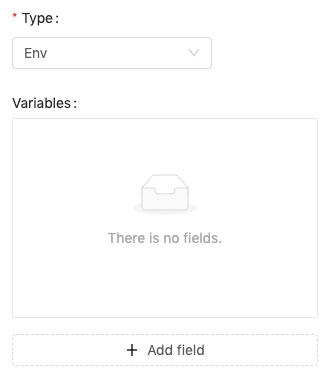
If volume is an environment variable, not a file, you can use env type. Clicking + Add field to add fields and fill the key and value.
Groups Access Control

Type, Global and edit groups are associated.
When
Typeof a volume is writable:Globalis enabled, required to specify groups with writable permission, the rest of groups are read-only.Globalis disabled, required to specify groups with writable/read-only permission respectively.
When
Typeof a volume is read-only:Globalis enabled, all of groups are read-only by default.Globalis disabled, required to specify groups with read-only permission.
In terms of type pv, nfs and hostpath volume, we can turn on Upload Server feature on the volume editing page. See Upload Server.